H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Rotational Mechanics, Exercise 2: OBJECTIVE I
H C Verma Physics Solutions for Exercise - H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Rotational Mechanics, Exercise 2: OBJECTIVE I
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 10: Rotational Mechanics, Exercise 2: OBJECTIVE I with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. CONCEPTS OF PHYSICS [VOLUME 1] solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Rotational Mechanics, Exercise 2: OBJECTIVE I with Hints & Solutions
A person sitting firmly over a rotating stool has his arms stretched. If he folds his arms, his angular momentum about the axis of rotation
The centre of a wheel rolling on a plane surface moves with a speed . A particle on the rim of the wheel at the same level as the centre will be moving at which of the following speeds?
A wheel of radius is pushed to move on a rough horizontal surface. It is found to move through a distance of on the road during the time it completes one revolution about the centre. Assume that the linear and the angular accelerations are uniform. The frictional force acting on the wheel by the surface is
The angular velocity of the engine (and hence of the wheel) of a scooter is proportional to the petrol input per second. The scooter is moving on a frictionless road with uniform velocity. If the petrol input is increased by , the linear velocity of the scooter is increased by:
A solid sphere, a hollow sphere and a disc all having same mass and radius, are placed at the top of a smooth incline and released. The least time will be taken in reaching the bottom by:
A solid sphere, a hollow sphere and a disc all having the same mass and radius, are placed at the top of an incline and released. The friction coefficients between the objects and the incline are same and not sufficient to allow pure rolling. The least time will be taken in reaching the bottom by:
A solid sphere, a hollow sphere and a disc all having same mass and radius are placed at the top of an incline and released. The friction coefficients between the objects and the incline are same and not sufficient to allow pure rolling. The smallest kinetic energy at the bottom of the incline will be achieved by?
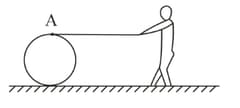
A string of negligible thickness is wrapped several times around a cylinder kept on a rough horizontal surface. A man standing at a distance from the cylinder holds one end of the string and pulls the cylinder towards him. There is no slipping anywhere. The length of the string passed through the hand of the man while the cylinder reaches his hands is